On this page
AIDE for TufinOS 4
Overview
Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment (AIDE) is an open-source utility that creates a database of files on the system and uses that database to ensure file integrity and detect system intrusions.
This procedure describes configuring periodic checking of the file system integrity to detect changes. Periodic file checking allows the system administrator to determine if there are unauthorized changes to critical files.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, log in as a root user with the root user environment variables. If you logged in as a regular user, you can become a root user, including the root user environment variables, by using the sudo su - command. If the sudo command is not configured, you can use the su - command.
Check AIDE Configuration
Run the commands below. If the output of one or more of these commands is not as expected, follow the steps in Configure and Schedule the AIDE Check).
-
The expected output for this command is static:
-
The expected output for this command is enabled:
-
The expected output for this command is active:
-
The expected output for this command is CONTENT_EX:
Configure and Schedule the AIDE Check
Perform this procedure if the output of one or more of the commands in Check AIDE Configuration is not as expected.
-
In the
/rootdirectory, disable AIDE extended content files check: -
Verify that the AIDE configuration has been changed as expected:
This command should return CONTENT_EX:
-
Remove existing AIDE databases:
-
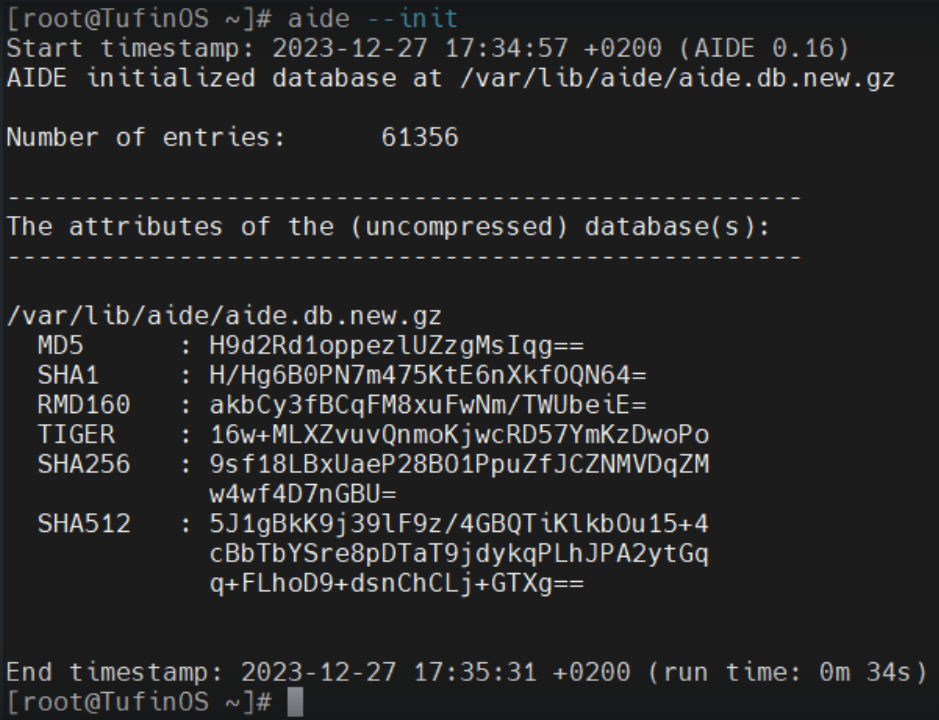
Initialize the AIDE database. This process might take a while.
The AIDE database is initialized.
-
Rename the new AIDE database:
-
Create a service file
/etc/systemd/system/aidecheck.serviceto run the AIDE check. Copy/paste the following content to the file: -
Save the service file.
-
Create a timer file
/etc/systemd/system/aidecheck.timerto schedule the AIDE check. Copy/paste the following content to the file. If required, you can change the scheduled run time from 02:00 AM to a different value. -
Change permissions and ownership of the service and timer:
-
Reload the systemd daemon:
-
Verify that the files you created do not contain any errors:
systemd-analyze verify /etc/systemd/system/aidecheck.*systemd-analyze verify /etc/systemd/system/aidecheck.*If the command returns no output, the files passed the verification successfully.
-
Enable and start the AIDE check timer:
-
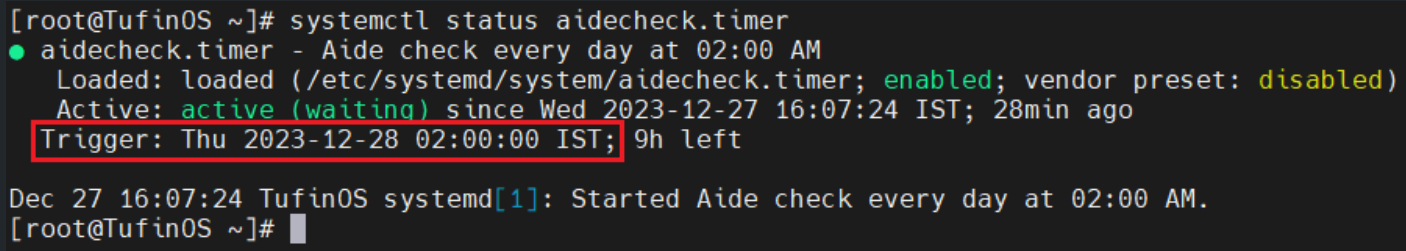
Verify the AIDE check timer status:
The AIDE timer details appear:
-
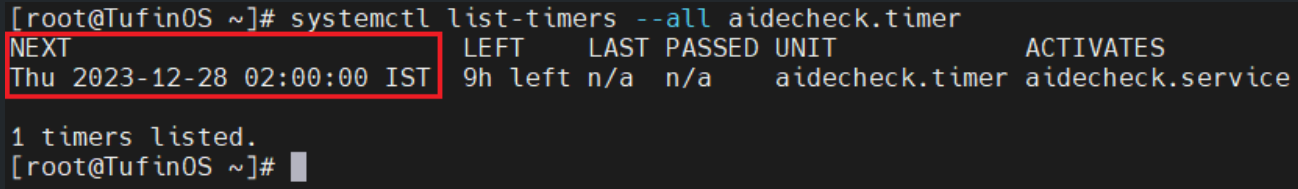
Verify that the AIDE check timer is in the timers list:
For example:
Run the AIDE Check Manually
Start the AIDE service:
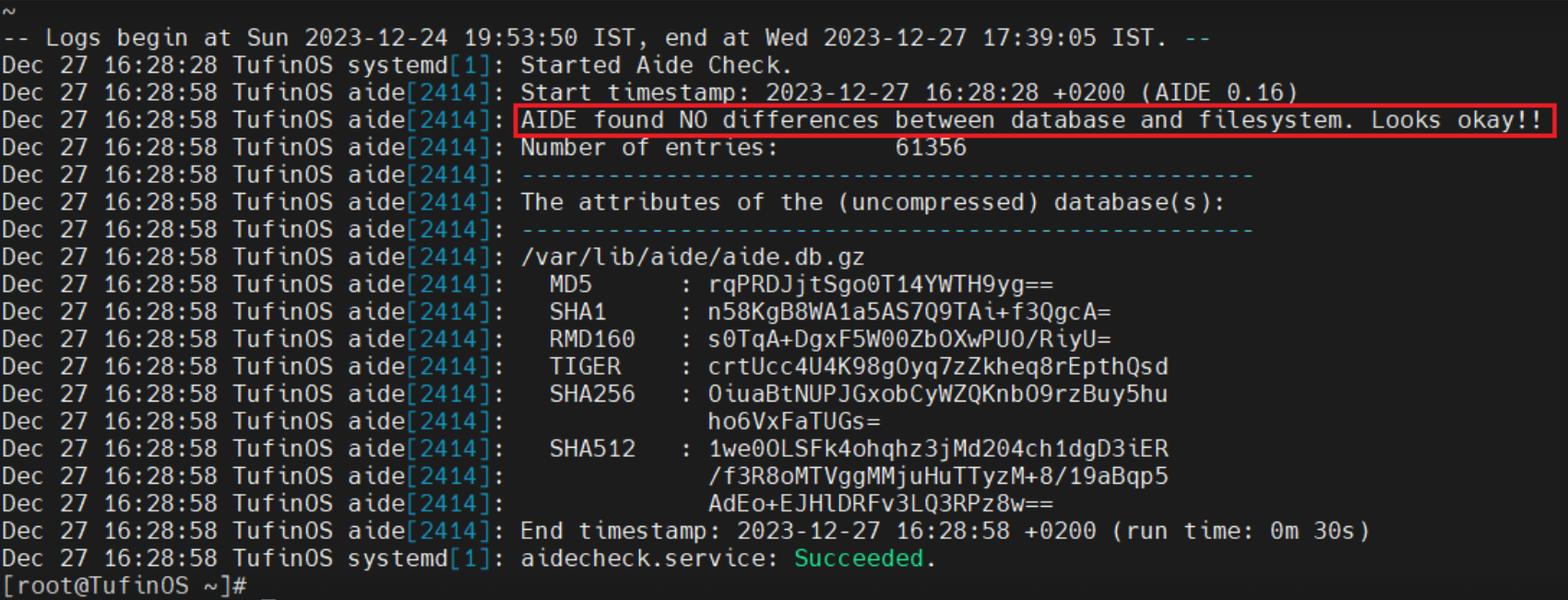
Run the journalctl command:
If there are differences between the AIDE database and the file system, they will appear in the log results.
If there are no differences, the log message "AIDE found NO differences between database and filesystem. Looks okay!!" will appear.
Was this helpful?
Thank you!
We’d love your feedback
We really appreciate your feedback
Send this page to a colleague