On This Page
Map
Overview
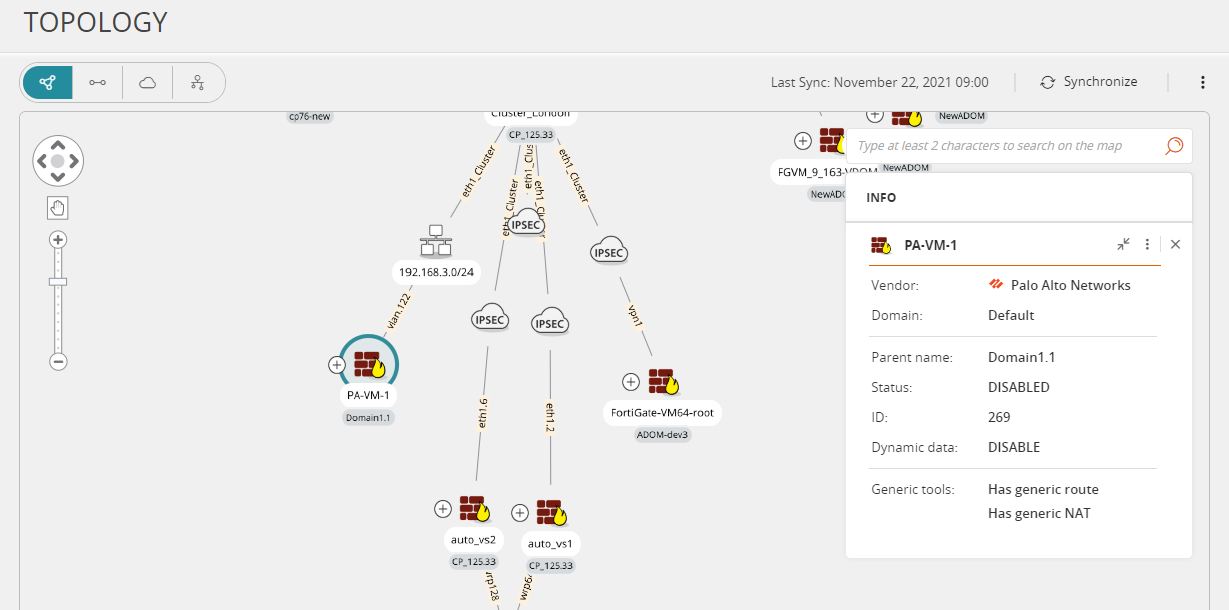
The Map (also known as the network map), is a dynamic map of your monitored devices and the subnets to which they are connected. The map is created using Topology Intelligence.
You can enter the details of a network traffic flow to see the path of the traffic on the map.
The Map includes:
|
Object |
Description |
Actions |
|---|---|---|
|
Cloud
|
A group of subnets for which a device routes traffic through an interface to an unknown gateway. The default name of the cloud includes the gateway listed for the routes. |
Right click a cloud to see the known subnets that are in the cloud. For a cloud, you can:
|
|
|
Public cloud: Azure Vnet, AWS VPC, or NSX-T. |
Right-click a public cloud to display its associated routes and subnets. Click |
|
|
A network device that is not monitored by SecureTrack but is included in topology calculations. |
Click a generic device to see its interfaces, IP addresses and routing table. For a generic device you can:
|
|
Monitored Device
|
A network device that is monitored by SecureTrack. The names of the interfaces are shown on the connections from the device. |
Click a device to see its interfaces, IP addresses and routing table. |
|
Subnet
|
A network subnet that is connected to at least one device interface. |
Click a subnet to see the device interfaces that are connected to it and the IP addresses of the interfaces. For a subnet, you can:
|
|
Subnet and Cloud Groups
|
A group of subnets or clouds that are all only connected to one monitored device. |
Click |
|
Connectivity between virtual systems
|
Connectivity between two virtual systems (such as virtual firewalls for Panorama) |
None |
|
|
F5 devices |
|
|
|
A connection that is established over IPSEC. |
None |
|
|
Policy-based routing (PBR) for Cisco IOS routers |
None |
|
|
EVPN network infrastructure. Any device that has VXLAN participation will be connected to the EVPN cloud. |
None |
|
|
A peering connection: Azure, AWS, GCP
|
None |
|
|
|
None |
|
|
MPLS network infrastructure. Any device that has MPLS participation will be connected to the MPLS cloud. |
None |
|
|
Cisco ACI |
Right-click a Cisco ACI device to display its associated routes and subnets. Click |
|
|
Internet outbound link: Indicates traffic that goes out to the Internet only (no inbound traffic). |
|
Prerequisites
- Make sure that all of the devices that impact your topology are monitored by SecureTrack.
For devices that are not monitored, you can add a generic device to represent the device with its interfaces and routes.
-
Permissions
Access to the map is given only to users with sufficient permissions. The menu option Map
 will appear only for these users:
will appear only for these users:
Limitations
-
SecureTrack+ users can only view the map and its objects, and perform topology syncs. All other topology features are disabled.
-
Users without Administrator permissions, and with the Any device permission:
-
Cannot add generic interfaces, generic routes, generic VPNs, or transparent firewalls
-
Can only access the Map in single-domain environments
-
What can I do on this Page?
-
View the Map: Click
 to view and navigate the Map.
to view and navigate the Map. -
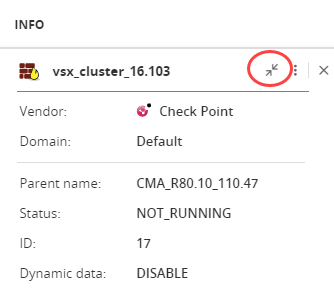
View device details: Click
 to expand and
to expand and  to collapse device details in the INFO panel.
to collapse device details in the INFO panel.Click
 to show the available device options:
to show the available device options:-
Show routes
-
Show interfaces
-
Show route base VPNs
-
Show peering information
Click
 to close the INFO panel.
to close the INFO panel. -
-
View cloud suggestions: Click the
 link in JOIN CLOUDS
link in JOIN CLOUDS -
Investigate traffic paths: Click
 to investigate a specific traffic path or to Diagnose Broken Traffic Paths.
to investigate a specific traffic path or to Diagnose Broken Traffic Paths. -
Join or split subnets: Click
 to join or split subnets
to join or split subnets -
Join or split clouds: Click
 to join or split clouds
to join or split clouds -
-
Grouped by Domain: Click Domain to group the devices in the map by domain. Relevant for users with Super Admin permissions.
-
Grouped by custom views: Click Custom View to group the devices in the map by custom views
-
-
Create and manage custom views for grouping devices: Click
 and select whether to add a new custom group or manage the custom views.
and select whether to add a new custom group or manage the custom views. -
Refresh the map: Click
 to synchronize the Map
to synchronize the Map -
Add generic device: Click
 and select Add generic device to enter the details for a generic device.
and select Add generic device to enter the details for a generic device. - Add Transparent Devices: Click
 and select Add transparent firewall to enter details for transparent devices.
and select Add transparent firewall to enter details for transparent devices. -
Export Map: Click
 and select one of the export options: PNG, PDF, Visio.
and select one of the export options: PNG, PDF, Visio. -
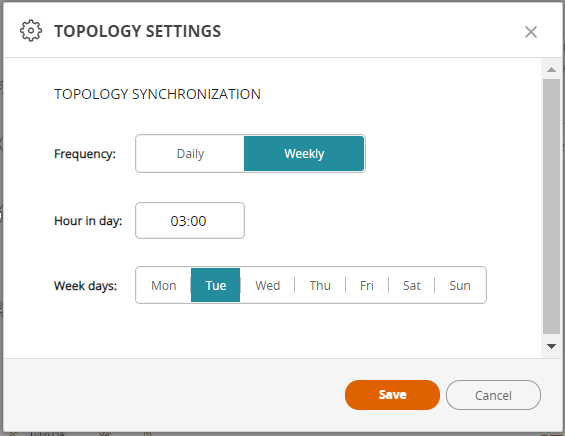
Topology Settings: Click
 and select this setting to define when SecureTrack collects topology information from enabled devices.
and select this setting to define when SecureTrack collects topology information from enabled devices.The default frequency to run the topology synchronization is every morning at 03:00. You can change the frequency (weekly/daily), time and the day of the week when it will run.
The backup and topology synchronization processes should not run at the same time. To prevent these processes from running simultaneously:Before backing up your database, check that the topology synchronization is not running.
Schedule the Backup and Topology Synchronization to run at different times when there will be no overlap between the two processes.
-
Multi-domain only: Click
 to switch domain contexts and view the devices for a specific domain. Users with "Super admin" permission can also view the Global domain context (see Multi-Domain Management).
to switch domain contexts and view the devices for a specific domain. Users with "Super admin" permission can also view the Global domain context (see Multi-Domain Management).
Page Controls
Use these controls to navigate in the map page.
|
Control |
Description |
|---|---|

|
Use the arrows to pan around the map, sliding the view up, down, right or left. |
 / /  |
Use the hand to slide the map. Click the hand to toggle to the arrow, which you use to highlight a group of objects in the map. |

|
Use the slider or +/- buttons to control the zoom level of the map. |
How Do I Get Here?
SecureTrack > Map ![]() .
.

 to see the subnets.
to see the subnets.